The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency and Honda R&D to begin feasibility study to supply oxygen, hydrogen, and electricity for outposts and rovers.
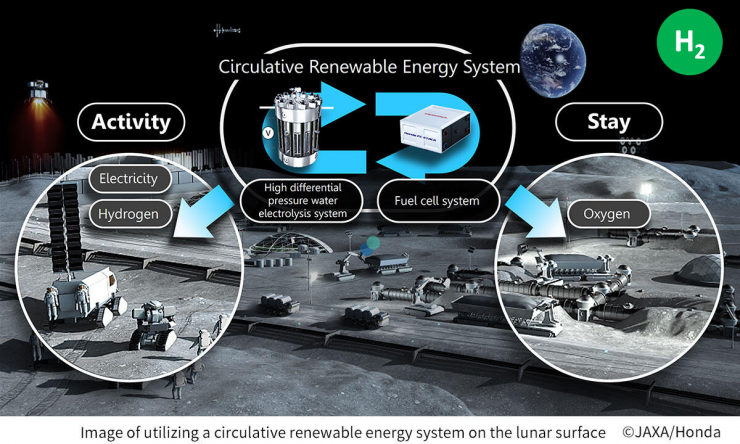
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and Honda R&D Co., Ltd. (Honda) announced the plan to begin a joint feasibility study on a “circulative renewable energy system” in space, which is designed to supply oxygen, hydrogen, and electricity for human outposts and rovers.
JAXA and Honda have been conducting a joint research on this system to create an environment in space where people can stay and conduct activities over an extended period of time.
In addition to water and food, people need oxygen, as well as hydrogen for fuel and electricity for various activities for life in space.
🔥 What about we co-host a webinar? Let's educate, captivate, and convert the hydrogen economy!
Hydrogen Central is the global go-to online magazine for the hydrogen economy, we can help you host impactful webinars that become a global reference on your topic and are an evergreen source of leads. Click here to request more details
One of the solutions to obtain them in space without resupply from Earth is creating a circulative renewable energy system, which combines a high differential pressure water electrolysis system that produces oxygen and hydrogen using solar energy to electrolyze water and a fuel cell system that generates electricity and water from oxygen and hydrogen.
Based on this concept, in November 2020, JAXA and Honda signed a three-fiscal year joint research agreement (through JFY 2022) to pursue research on the circulative renewable energy system for use on Lunar Orbital Platform-Gateway (Gateway) and on the surface of the Moon, utilizing Honda’s high differential pressure water electrolysis and fuel cell technologies.
In this joint research, while JAXA has been developing the study conditions according to the scenarios and requirements for missions related to the production of oxygen on the Gateway and the supply of electricity to rovers on the lunar surface based on the past investigations, Honda has been conducting technological studies to realize the missions and scenarios set by JAXA.
During the current fiscal year (JFY 2021), JAXA and Honda, utilizing the prototypes, will start the feasibility study addressing the issues on component technologies of the circulative renewable energy system identified by the research conducted during the last fiscal year. JAXA and Honda are planning to reflect the results of this year’s study on the viability evaluation of the whole system in the next fiscal year (JFY 2022).
Comments by JAXA and Honda executives
SASAKI Hiroshi, JAXA Vice President and Director General for Human Spaceflight Technology Directorate:
Based on the Japanese Government’s decision to participate in the Artemis program, JAXA has been working on mission development and system studies for realizing full-fledged lunar exploration.
“Oxygen, hydrogen, and electricity are essential to human activities in space. Realizing a circulative renewable energy system will enable us to obtain these requirements in space without relying on resupply from Earth. This is expected to dramatically expand our activities in space. We would like to make steady progress in this study by leveraging the respective strengths of Honda and JAXA.”
TAKEISHI Ikuo, Chief Operating Officer, Innovative Research Excellence, Power Unit & Energy, Honda R&D Co., Ltd.:
Honda is striving to realize an enjoyable and sustainable society and to serve people worldwide with the joy of expanding their life’s potential, on the ground, in the ocean, in the skies and in space.
“Through this joint research we are taking on a challenge to utilize technologies we have amassed to date and expand the sphere of human habitation into outer space, which will expand human potential. Moreover, since the circulative renewable energy system will contribute significantly to carbon neutrality on Earth, we will refine our technologies in the ultimate environment of outer space and then feed our achievements back to Earth.”
READ the latest news shaping the hydrogen market at Hydrogen Central
JAXA and Honda to Begin a Feasibility Study on a Circulative Renewable Energy System, June 14, 2021