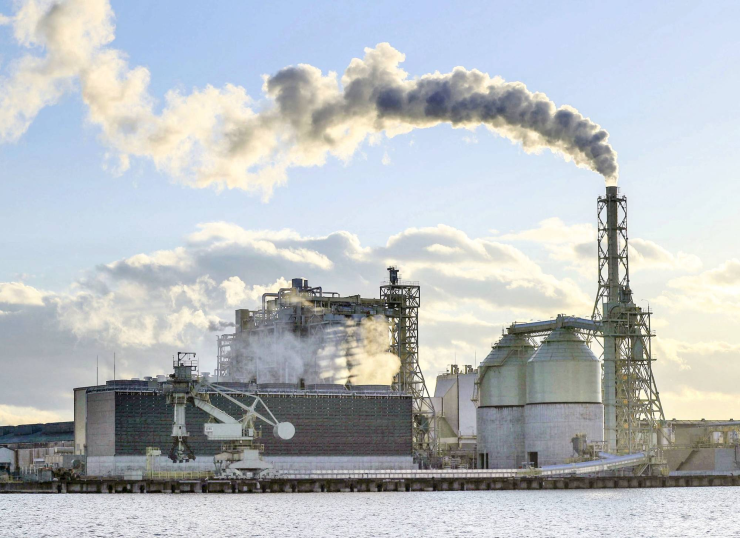
Japan – its hydrogen economy runs the risk of being powered by coal.
It’s no secret that Japan is betting on hydrogen as a clear and inexperienced power supply.
Japan was the primary nation on this planet to launch a nationwide hydrogen technique, with then-Prime Minister Shinzo Abe unveiling the coverage in 2017.
Since then, greater than 30 nations and areas — together with South Korea, Australia, the UK and the European Union — have adopted swimsuit, demonstrating an acceleration of presidency curiosity within the position of hydrogen as a part of a nation’s long-term power targets.
🔥 What about we co-host a webinar? Let's educate, captivate, and convert the hydrogen economy!
Hydrogen Central is the global go-to online magazine for the hydrogen economy, we can help you host impactful webinars that become a global reference on your topic and are an evergreen source of leads. Click here to request more details
Eiji Ohira, director common of the gasoline cell and hydrogen know-how workplace on the New Power and Industrial Expertise Growth Group (NEDO), said:
Hydrogen is essential for sustainable growth.
“It may be produced from quite a lot of sources, doesn’t emit greenhouse gasses when used and will help to energy numerous totally different sectors.”
Japan in the end goals to change into the world’s first “hydrogen financial system,” with the chemical aspect more and more portrayed as a significant cog within the nation’s efforts to achieve its long-term purpose of zero carbon emissions by 2050.
However that focus on stays a good distance off. Fossil fuels account for greater than 80% of Japan’s present power provide, of which 32% comes from coal energy vegetation.
This locations Japan because the sixth largest shopper of coal on this planet, an power supply that alone produces one-fifth of worldwide greenhouse fuel emissions every year.
Moreover, the Japanese authorities’s goal to cut back the share of coal to 19% of the nation’s power combine by 2030 is broadly thought-about inadequate to satisfy its decarbonization targets and, in the end, the Paris Settlement purpose of limiting world warming to under 2 levels Celsius.
Japan – its Hydrogen Economy Runs The Risk of Being Powered by Coal
Evan Gach, program coordinator at Kiko Community, a nonprofit environmental group working to forestall world warming, said:
Coal remains to be the most important supply of Japan’s CO2 emissions.
“Most individuals see coal as a factor of the previous and are shocked to know that, not solely is it nonetheless getting used, however that there are plans to start working new coal-fired energy models throughout the nation.”
‘Clear coal’ debate
Critics of the federal government’s power coverage have questioned the competing nature of Japan’s home local weather commitments with its funding in new coal-fired energy vegetation at dwelling and overseas.
Power officers sometimes level to latest technological advances that permit coal for use to make hydrogen whereas capturing and storing the dangerous emissions generated within the course of, in addition to the potential to make use of hydrogen or ammonia in energy vegetation that may burn several types of gasoline on the similar time.
However Yasuko Suzuki, program coordinator at Kiko Community, says that such arguments don’t paint the total image of what’s taking place right here.
Suzuki says.
Numerous authorities subsidies are being funneled within the path of ‘clear coal,’ together with monetary help for the manufacturing of hydrogen and the event of associated tools.
“Nevertheless, fossil fuels will proceed to be burned even when new know-how is getting used within the course of and carbon will proceed to be launched into the air. There is no such thing as a such factor as clear coal.”
Local weather campaigners argue that Japan’s hydrogen financial system should transfer away from being depending on fossil fuels or else it’s going to find yourself giving coal a brand new lease on life.
The Matsushima Thermal Energy Plant within the metropolis of Saikai, Nagasaki Prefecture, is a living proof. Constructed greater than 40 years in the past, it is without doubt one of the oldest coal-fired energy vegetation within the nation. It was slated for mothballing by 2030, though official dates have by no means been introduced.
Nevertheless, the operator of the power has rolled out plans to retrofit the plant in order that it may possibly run on a combination of coal and hydrogen till the know-how to burn carbon-free hydrogen is carried out.
“Retrofitting the oldest vegetation in Japan will merely prolong the lifetime of coal vegetation with out meaningfully decreasing emissions,” Gach says.
“By doing so, Japan’s hydrogen technique is basically simply protecting coal energy alive and, if pursued at the price of shifting to renewable power, Japan will probably be locked into the long-term use of fossil fuels and CO2 emissions.”
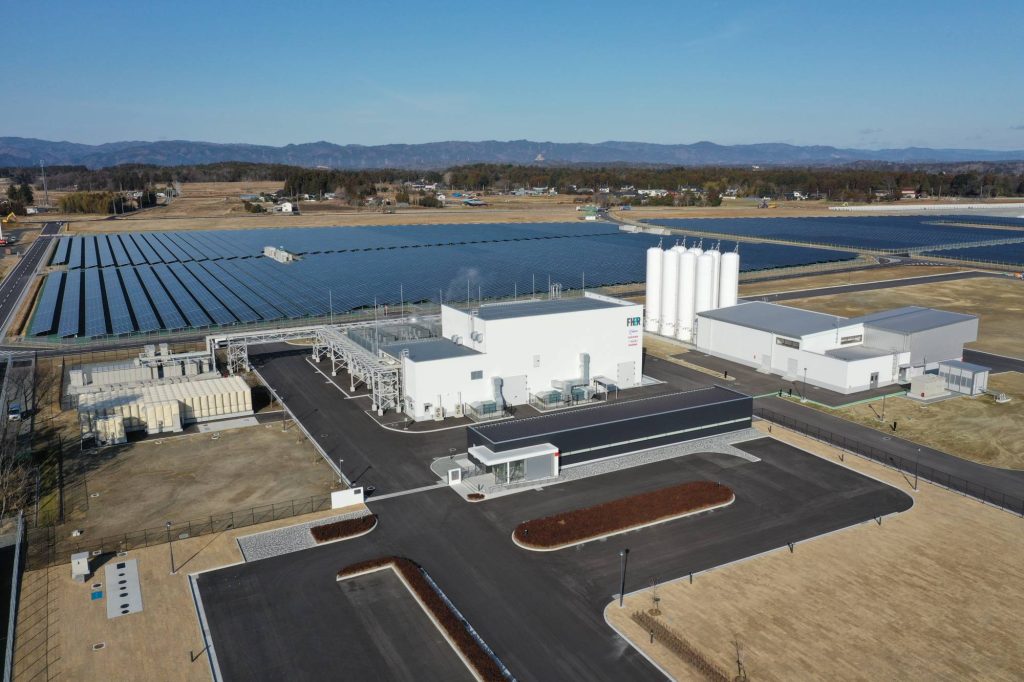

Yuko Nishida, senior supervisor on the Renewable Power Institute, an impartial suppose tank that has been working to advertise local weather neutrality and renewable power in Japan, claims the present deal with hydrogen is a critical concern.
Though Nishida sees advantages in utilizing hydrogen in restricted roles in particular sectors, she says that an overreliance on the aspect — whose power effectivity is low and prices are excessive — quantities to betting on a shedding horse, notably if the manufacturing, transportation and storage of hydrogen are factored in.
“Hydrogen will play an necessary half in our power combine sooner or later, however provided that we’ve got a correct plan for the place it comes from and the way we put it to use,” Nishida says. “We should differentiate between several types of hydrogen.”
Japan – its Hydrogen Economy Runs The Risk of Being Powered by Coal – The hydrogen palette
Hydrogen is essentially the most plentiful aspect within the universe. On Earth, it’s present in water, vegetation, animals and even people. With the intention to be used as a gasoline, nonetheless, it must be separated from different molecules — a course of that requires power.
Which means, though hydrogen emits no dangerous gasses when burned, its environmental credentials additionally rely on the tactic used to supply it within the first place.
At the moment, world hydrogen manufacturing depends virtually solely on pure fuel or coal, producing extra carbon dioxide emissions than the entire of the UK and France mixed. This sort of hydrogen is usually known as grey hydrogen.
In distinction, hydrogen obtained from water utilizing renewable power is named inexperienced hydrogen, which presently makes up lower than 0.1% of worldwide hydrogen manufacturing because of the excessive value of renewable power and electrolysis know-how — the method of splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen — which remains to be within the early phases of growth.
To beat issues plaguing each grey and inexperienced hydrogen — the previous’s emissions and the latter’s comparatively excessive prices — Japan’s hydrogen technique focuses on blue hydrogen, which is produced utilizing fossil fuels however depends on experimental applied sciences to seize and retailer the carbon emissions which are generated throughout manufacturing.
Blue hydrogen is taken into account notably engaging as a result of it allows power firms to proceed to make use of low cost fossil fuels and present coal-fired energy vegetation that may in any other case face closure as a part of efforts to decrease emissions.
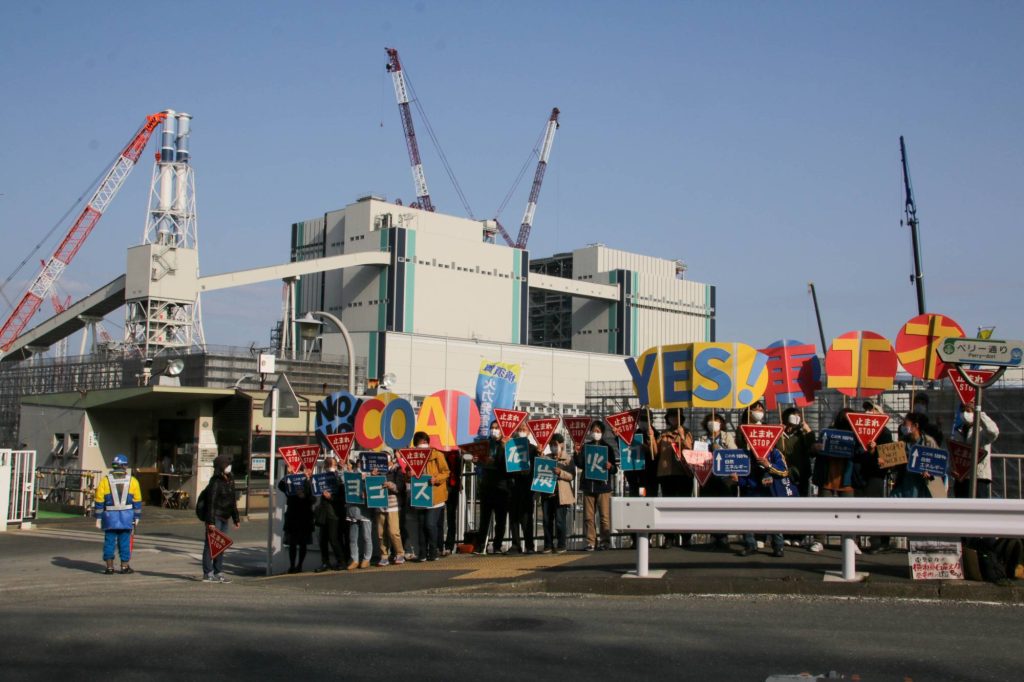

Enterprise as standard
Toshikazu Ishihara, senior researcher on the Renewable Power Institute, said:
The federal government is simply far too optimistic about applied sciences that seize and retailer carbon emissions.
“Not solely are these applied sciences largely unproven however, notably in Japan, we merely don’t have sufficient appropriate locations to retailer the massive quantities of carbon that may have to be captured.”
Carbon seize and storage works by trapping the carbon emissions generated in the course of the burning of fossil fuels and storing them in a secure place the place they won’t leak again into the environment. The emissions are often stored deep underground in geological formations reminiscent of outdated fuel or oil reserves.
Nevertheless, Japan has only a few sensible places for this type of storage and any areas that would probably be used are both located removed from industrial facilities — making transportation costly and inefficient — or in danger because of the nation’s excessive publicity to seismic exercise, which might probably result in saved carbon leaking again into the environment.
“Blue hydrogen with carbon seize and storage is just not sustainable. It merely sweeps the issue underneath the carpet, leaving it for the following generations to cope with,” Nishida says.
“In Japan — the place we don’t have appropriate places to retailer giant quantities of CO2 — the present deal with blue hydrogen is extra about enterprise continuity and protecting the prevailing power system in place than carbon neutrality.”
A big a part of Japan’s hydrogen technique presently revolves round creating a hydrogen provide chain — engaged on tasks in nations which are resource-rich and have extra appropriate places for hydrogen era — after which importing hydrogen for use as a gasoline.
“Japan desires to pioneer this technological push,” Nishida says.
“China gained the race to develop photo voltaic know-how and electrolyzers for inexperienced hydrogen, so the Japanese authorities is now new hydrogen applied sciences as the following huge alternative.”
Nevertheless, latest tasks to implement carbon seize and storage have up to now didn’t ship on their guarantees, with low charges of carbon seize and excessive working prices.
In a single such endeavor involving Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd., Iwatani Corp. and Australian firm AGL Power Ltd., blue hydrogen is produced from coal within the state of Victoria earlier than being liquified and transported to Japan.
Nevertheless, dangerous gasses generated within the manufacturing course of are launched into the environment, and future carbon seize methods stay imprecise and unproven.

What’s extra, specialists argue that Japan’s deal with blue hydrogen runs the danger of leaving the nation reliant on gasoline imports from overseas, exacerbating underlying power safety points — a subject that’s extra related than ever within the wake of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the ramifications this has had on power safety in Europe and past.
“Traditionally, Japan has been extremely depending on fossil gasoline imports,” Nishida says.
“This can be a safety concern for the nation and plans to import hydrogen will solely proceed this development.”
But issues associated to power safety should not particularly tied to blue hydrogen.
Jane Nakano, a senior fellow on the Middle for Strategic and Worldwide Research who lately revealed a paper on Japan’s industrial hydrogen technique, said:
Whether or not it’s blue or inexperienced hydrogen, Japan will doubtless proceed to rely on overseas power imports.
“On the present value ranges, hydrogen use doesn’t current an financial benefit over different types of power in Japan.”
Nishida believes the nation may gain advantage from larger funding in renewables throughout the board.
“What Japan actually wants is to prioritize creating renewables, and inexperienced hydrogen will be part of that course of,” Nishida says.
The inexperienced motion
Within the city of Namie, Fukushima Prefecture, NEDO is working to develop power-to-gas know-how on the Fukushima Hydrogen Power Analysis Area in an effort to enhance electrolysis know-how and discover methods of creating low-cost, clear hydrogen manufacturing.
The power is dwelling to the most important hydrogen manufacturing unit on this planet, offering beneficial perception on the long run position of inexperienced hydrogen.
Ohira says, said:
Hydrogen is extraordinarily beneficial by way of power storage as a result of it shops electrical energy in the identical method {that a} battery does.
“That is notably necessary within the context of accelerating renewables as a result of it may possibly assist cut back imbalances between provide and demand that naturally happen with wind and photo voltaic.”
Moreover, hydrogen might change into extraordinarily helpful in a fancy power system that makes area for localized power manufacturing.
“Think about a hydrogen refueling station that produces its personal hydrogen onsite utilizing small-scale electrolysis with native renewable power,” Ohira says. “This might remove the prices of transporting gasoline to locations which are removed from giant manufacturing websites.”

Nevertheless, inexperienced hydrogen presently suffers from the identical points plaguing renewable power in Japan: excessive prices and inadequate provide.
“The primary barrier to inexperienced hydrogen is the worth of electrical energy, particularly by way of renewable electrical energy,” says Ohira, who provides that water electrolysis know-how remains to be in its infancy and that there’s a want to enhance effectivity and sturdiness so as to cut back prices additional.
This has led some to argue that Japan ought to use blue hydrogen as a stepping stone to realize long run plans to scale up hydrogen manufacturing.
“If we produce hydrogen with fossil fuels, then we are able to obtain economies of scale and decrease manufacturing prices,” says Ohira, who believes that Japan’s future power system would require a combination of power sources, together with each blue and inexperienced hydrogen. “With inexperienced hydrogen, it is a lot tougher.”
“We will increase manufacturing however the price of water electrolysis models is basically linear because of the nature of the system.”
Nevertheless, not everybody agrees with this technique.
“It’s paramount that hydrogen is produced in an environmentally sustainable and local weather benign method to maximise emissions discount advantages throughout a variety of sectors,” Nakano says.
Moreover, Nishida says that it’s necessary to behave in ways in which be sure that Japan’s long-term power targets are achieved. Thanks for staying up to date with Hydrogen Central.
“Grey and blue hydrogen hold the fossil gasoline era system afloat and the applied sciences used don’t relate to inexperienced hydrogen manufacturing,” Nishida says.
“We can not afford to waste time. The actual precedence needs to be to spend money on renewables and, as soon as these are developed, then we are able to discuss scaling up hydrogen.”
Japan’s ‘hydrogen economy’ runs the risk of being powered by coal, April 18, 2022