All there is to know about hydrogen fuel cells – Renault Group.
In an effort to drive sustainable mobility, Renault Group is turning to cleaner technology and engines, such as that used on traditional electric cars, but also hydrogen fuel cell cars. By combining fuel cells with ‘green’ hydrogen, Renault Group is ushering in a new era for mobility, a necessary shift for the coming decades. While still relatively small for the time being, it is a market that is constantly growing.
There are multiple advantages to running vehicles on hydrogen fuel cells: cars emit only water vapour, run silently, offer a driving range and performance that are on par with current cars, and take only 3 to 5 minutes for a complete refill. How does a car with a hydrogen fuel cell work? What are the main issues with this new form of mobility? Here is an overview of the Group’s latest hydrogen innovations.
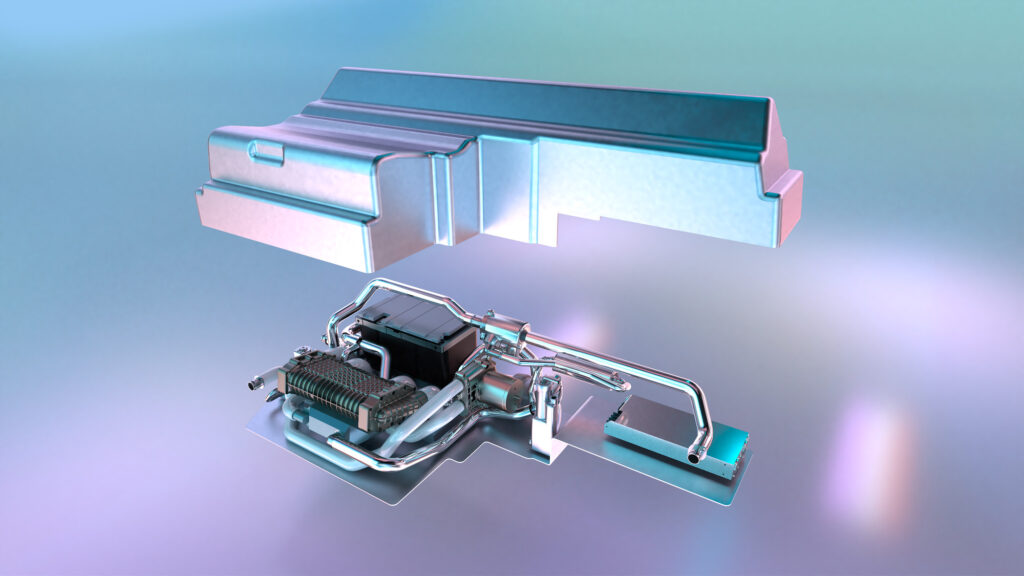
Fuel cells are still relatively unknown for many people. Known as energy converters, they directly transform fuel into energy, producing electricity, water, and heat. Hydrogen fuel cells are one of the most common types of fuel cell and run on a mix of hydrogen and oxygen.
🔥 What about we co-host a webinar? Let's educate, captivate, and convert the hydrogen economy!
Hydrogen Central is the global go-to online magazine for the hydrogen economy, we can help you host impactful webinars that become a global reference on your topic and are an evergreen source of leads. Click here to request more details
Thanks to their low environmental impact, the technology has piqued the interest of automotive manufacturers looking for sustainable mobility solutions for a cleaner, carbon-free future. So, how does it work? And what advantages are there to using it on a daily basis?
How does a fuel cell work?
The way a fuel cell works is quite simple and is based on an electrochemical reaction called oxidation-reduction (redox). A fuel cell comprises two electrodes: an oxidizing anode that emits electrons and a reducing cathode that collects electrons. Catalysts are used to separate the two electrodes from a central electrolyte, which can be either liquid or solid and helps ions move about.
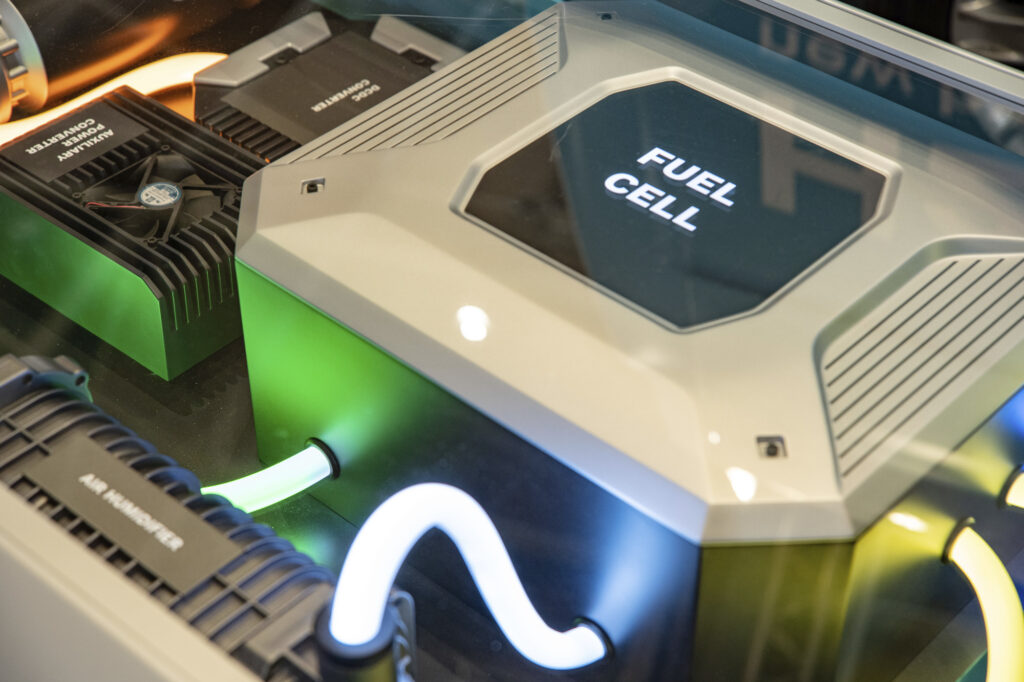

In the case of a hydrogen fuel cell, hydrogen is converted into electricity. Inside the anode, a catalyst breaks down hydrogen into electrons and hydrogen ions. Hydrogen ions pass through the electrolyte to the cathode, while electrons pass through an electrical circuit, thus creating the electrical energy that powers the electric motor and battery.
Inside the cathode, the catalyst helps oxygen from the surrounding air to combine with electrons coming from the electrical circuit, thereby creating oxygen ions. When they mix with hydrogen ions from the electrolyte, they form water molecules – the fuel cell’s only by-product. Fuel cells on cars generate the electric current needed to power the engine and recharge the battery, much like with electric vehicles.
Hydrogen vs. electric car: what is the difference?
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are part of the electric-car family, but they use a different source of energy: hydrogen. Thanks to a simple chemical reaction between oxygen and hydrogen molecules, the fuel cell supplies electricity to the engine and recharges the battery.
But what is the difference between a hydrogen car and a traditional electric car? Electric vehicles use lithium-ion batteries to ‘simply’ store electric energy taken from the grid each time they are plugged in. This is where hydrogen vehicles differ. Electricity required to run the powertrain is supplied by the fuel cell, which itself uses hydrogen stored on board the vehicle.
It powers a battery, which in turn powers the electric motor. Most hydrogen vehicles currently on the market are based on the fuel-cell principle and boast excellent charging speeds and greater autonomy.
When it comes to refuelling a hydrogen car, it requires dedicated refuelling stations with pumps that can very quickly inject high-pressure hydrogen gas into the car’s tank.

What is ‘green hydrogen’?
Hydrogen fuel cells are one of the technological solutions that will help boost electric-vehicle uptake. For hydrogen mobility to be sustainable, the hydrogen must be ‘green’; in other words, it must come from the electrolysis of water. If the electricity being used for the electrolysis process comes from a sustainable energy source such as solar or wind, the hydrogen is deemed ‘low carbon’.
Advantages to a hydrogen fuel cell car
There are many advantages to a hydrogen fuel cell car. It makes driving a stress-free experience and boasts all the advantages of driving an electric vehicle: lag-free acceleration, quiet driving, no vibrations, and access to low-emission zones in some cities.
A complementary addition to full-electric vehicles, hydrogen technology has the advantage of combining reduced refuelling times and neutral carbon emissions when driving. As such, long journeys are made easy with hydrogen refuelling taking only 3 to 5 minutes – an appealing alternative to full-electric models.
Renault Group and hydrogen fuel cells
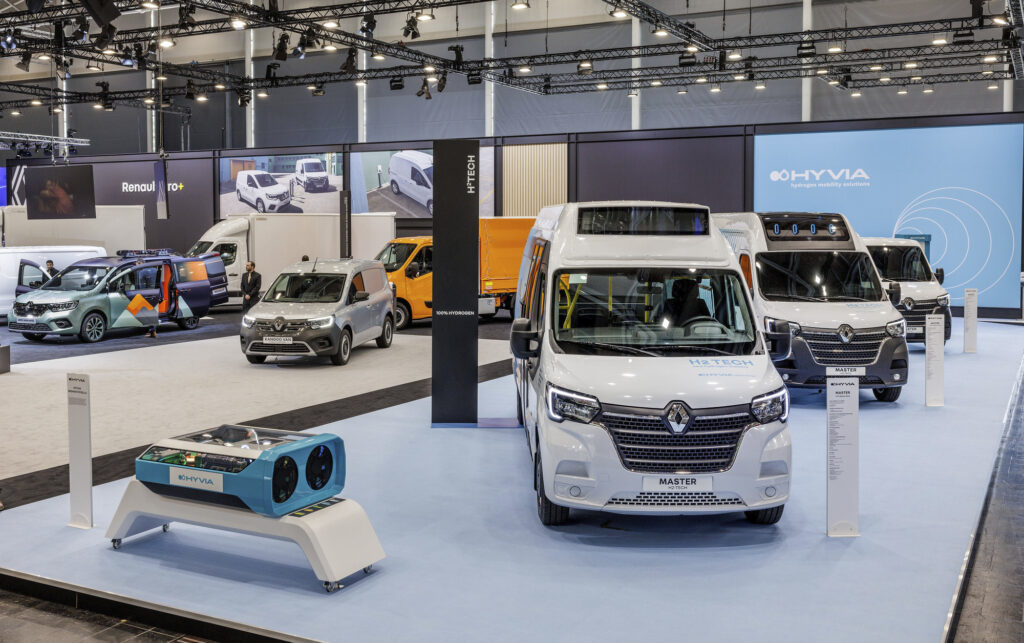
Renault Group has more than a decade of experience in designing, manufacturing, selling, and servicing electric vehicles. In an effort to take mobility to new horizons, it is turning to innovative technology, such as hydrogen fuel cells. Yet Renault already has experience with the technology. Used for the first time in 2014 to equip a vehicle in its utility line-up – the Renault Kangoo Z.E. Hydrogen –, it returned to the scene in 2021, with HYVIA, the hydrogen-mobility joint venture owned equally by Renault Group and Plug.
HYVIA now offers three LCVs with hydrogen fuel cell technology providing professional customers with low-carbon mobility that won’t impact their business: the Master Van H2-TECH, Master Chassis Cabin H2-TECH and Master City Bus H2-TECH. On these models, the fuel cell acts as a range extender when the battery (conventionally rechargeable) is partially discharged. It increases the vehicle’s range and meets the needs of commercial vehicle customers who are looking for long range, fast charging, zero-emission mobility.

HYVIA is extending its work in the field through the opening of its plant in Flins to provide French-based fuel-cell assembly lines, H2 charging stations, and low-carbon hydrogen production.

Pending the successful application of the technology to commercial vehicles, Renault is also exploring ways to harness it for private vehicles, capitalizing on the hydrogen networks that will have been developed. In 2022, Renault unveiled the Renault Scenic Vision, it’s very first private concept car featuring a unique electric-hydrogen hybrid engine, combining the advantages of fuel-cell and EV battery technology in a hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV).
All there is to know about hydrogen fuel cells, February 15, 2023









1 comment